You are living in Japan and you want to start your own export-import business in Japan but do not know how to start and how to become successful? Or you are living in some other country but considering do start an export-import business with Japan? Maybe you are interested to know what are potential products regarding Japan to import or export? Or perhaps you want to see the clear procedures for exporting or importing from Japan?
Well, in this article we will give you all the answers, resources and show you step-by-step how to start an export and import business in Japan or with Japan. We are also giving you many business ideas for your venture.
No matter what your purpose regarding the import-export business is, maybe you want to have a better life, want to earn more money, or simply want to satisfy your passion, we always uphold your decision and help you to succeed in this business.
With years and years of experience in the import-export business and international business, we will share with you the necessary knowledge and useful practical experience to help you build the foundation to start this exciting journey.
Based on our experience, if doing business with a new country, we shall learn about this country and its people first. So let’s have an overview of Japan first.
1. Overview of the Japanese business environment and economy
Japan is an island nation located in East Asia. The Japanese make up about 98.1% of the country’s total population. Nearly 13.8 million residents live in central Tokyo, the country’s unofficial capital. The Tokyo metropolitan region, including the capital and the provinces surrounding it, is the largest metropolis in the world with more than 35 million people and has the highest urbanized economy in the world.
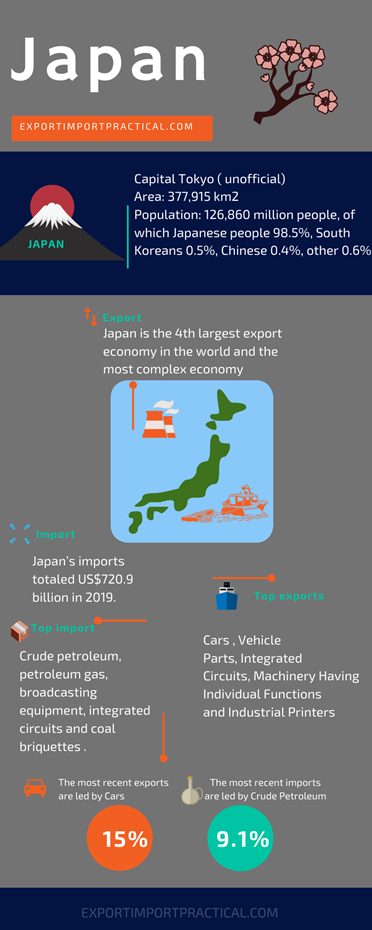
Japan’s economy is a developed market economy. In 2020, the size of the economy is the third largest nominal GDP measure in the world after the United States and China. While if we do the measurement of purchasing power parity, then Japan was the fourth largest after the United States, China, and India.
In the Japan-EU Free trade agreement (FTA), from 2035, the country will eliminate duties on about 94% of goods imported from the EU, Europe will also remove the tariff barriers in stages at same period.
This will create huge business opportunities for entrepreneurs on both sides.
Tokyo also started trade talks in 2019 with the US.
Japan is a country with an industrialized and high-tech developed economy reflected in its leading exports, focusing on products such as automobiles, optics, engineering, healthcare, and machinery, robotics. Japan has also a competitive advantage in exporting ships, boats, and other floating structures.
The main groups of Japanese exports are vehicles; machines; robots; electronic devices occupied; technical optics and medical equipment, iron and steel of all kinds; chemistry; plastic.
Japan’s largest export partners are China, USA, Korea, Thailand, Hong Kong.
Imported items are machinery and equipment, fuel, food, chemicals, textiles, and raw materials, especially mineral and energy products.
Importing partners are China, the USA, Australia, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, South Korea, etc.
The Japanese people characteristics
The Japanese have a very special personality. Perhaps thanks to these characteristics, the Japanese have turned their country of poor resources and harsh climate into a great power. Japanese characteristics are as follows:
- Having a progressive and sensitive spirit of changes in the world. Willing to accept new ways but still retains its identity.
- Enhance the common, the collective, dismiss the individual egos. The collective can compete with each other but can also work together to achieve common goals.
- They do not like to confront others, especially personal confrontation. They pay attention to harmony. Maintaining consensus, appearance, and reputation is important.
- Saving and working hard.
2.Pros and cons of doing international business with/in Japan

Pros of doing business in/with Japan
20 years ago, Japan fell into a state of stagnation and economic recession, but in recent years, through the reforms of the Government of the Japanese economy, the economy revived and accelerated in the coming time.
Japan is an attractive investment destination because it is one of the biggest markets regarding consumer consumption. The main indicator for this is the fact that Japan’s GDP is the third-largest in the world. The number of research and development expenses per capita of Japan is also ranked first in the world. This means Japan is a good place for setting up high-tech productions.
Infrastructure, communication systems, as well as transport systems in Japan, are also on the top level, convenient for businesses to travel.
For the Japanese market, new trading and reselling businesses have many opportunities. One idea, we would point out is related to the Japanese aging population. This means products for old and elderly people are in great demand there.
Cons of doing business with/in Japan
However, on the other hand, In terms of domestic factors, rapid population aging and low birth rates are currently the biggest challenges for Japan. Currently, Japan is struggling to cover the increasing costs of social security due to the increasing number of elderly people.
The cost for businesses to penetrate is very high, because the cost of accommodation, travel costs in Japan is quite high, on par with the EU or America. Technically, Japan has very strict regulations, so the goods exported to Japan must be guaranteed in terms of quality. This is a remarkable block for companies starting exporting to Japan from overseas.
Plus, when establishing a representative office in Japan, it is difficult to recruit Japanese engineers and workers, especially IT engineers because of the very high salaries. English is also not a common language of Japanese, so you need to prepare translators or self-study Japanese.
Besides, the current tensions and trade war between the two largest economies in the world China-USA also adversely affects large Japanese exporting and importing companies.
In addition, worsening trade relations between Japan and South Korea made Japan’s export activities more difficult to Korea.
Note: read also advantages and disadvantages of exporting.
3. Suggestions for new entrepreneurs regarding Japan
Doing import and export business directly, requires remarkable amount of capital, and requires to invest in goods and warehouses, staff, inventory. If you are financially not strong enough, or if you cannot find investors, you could start from the service sector.
Or why not to start as an export-import agent in Japan. As an agent, you can be a solopreneur, with minimal investment. It is a very lucrative business form currently and it is becoming more and popular. You can be an agent, bringing Japanese suppliers and overseas buyers together and/or vise-versa. You can take commission fees from each deal you help to close.
When starting a business or doing import-export business in Japan, the most important thing is to keep its reputation. The Japanese business community has companies that provide assessment services, give a reputation score, a company’s ability, and based on that data, partners will evaluate themselves for appropriate cooperation.
Therefore, special attention must be paid, especially for young companies, on-time deliveries, keeping promises, and disciplines of payments.
The legal environment for businesses in Japan is very clear, does not cause any difficulties, but in return needs you to “live and work” according to the law.
The Japanese are generally afraid of change, afraid of trying new things if the old ones are still useful to them, causing them to be very loyal to their domestic goods. That’s why selecting a good and “right” product to export to Japan is very important.
For new and fresh entrepreneurs looking to start an export-import business with Japan or in Japan, we suggest using the help of local consultants and agents.
4.What does Japan export?
If you are interested to select the right product for exporting from Japan, then this chapter will give you ideas and insights. The following categories are the main export categories and everyone should dig deeper to choose the specific product for export. Read also, how to choose a product for export.

Main export products of Japan
The export of machines and high-tech products has impacted Japan’s economic growth since 1960. The main export groups in Japan include:
- Cars of all kinds
- Gearboxes and parts, accessories of automobiles
- The electronic circuit of video recording equipment
- Boats transporting goods
- Printers and copiers of all kinds
- Optical equipment, measuring machines
- Chemicals, organic chemicals, additives
- Rubber and rubber products used in cars
- Phones and phone parts and components
- Steels
The main export markets of Japan: Are the United States, China, South Korea, Taiwan, China, European Union countries.
Situation in the main export industries
Although Japan’s export sector is growing strongly, its economy remains stagnant, coupled with the strong Yen and the weak demand of the domestic market, which are the major challenges facing the economy after a period of a worsening recession in the past.
Automobile
Japan is still the second-largest automobile exporter in the world after Germany and is making efforts to improve. Japanese car exports have declined slightly in recent years after years of growth. One reason for this is the labor costs, which is relatively high and rising. Also, the Yen currency is often volatile, leading to reduced exports.
Electronic components
The Japanese electronics industry is the largest consumer electronics industry in the world, although the market share of these Japanese companies is declining due to competition from South Korea, Taiwan, and China. Japan has companies that produce TVs, camcorders, audio and video players, etc.
The Japanese electronics industry has maintained its dominance in the market compared to the United States and maintained its export power in this sector thanks to the high reputation of the electronics industry.
Industrial machinery
Japan is one of the most developed countries in terms of machinery. Japan’s automation industry is famous in the World for its high-quality machine manufacturing brands. Japan is a country with strengths in CNC machines because this country has workers who have in-depth knowledge of automation industrial machinery. Machines of Japanese brands are widely known, especially in Europe. The United States is also becoming a major importer of Japanese industrial machines. The increase in world demand for machinery and robotics opens up opportunities for manufacturing plants in Japan.
Thanks to the quality of the machine-made in Japan, buying old CNC machines is also very popular. Old machines are usually purchased by small businesses worldwide. These are the businesses that have a small budget to invest in production. Of course, the quality will not be guaranteed like buying a new CNC machine.
Japanese shipping industry
From the 1950s to the beginning of the 21st century, Japan and South Korea were the top two countries in the three indicators mentioned above, but since 2010, China has taken the lead in the shipbuilding industry.
Currently, Japan has more than 1100 shipyards. Leading shipbuilders such as Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd. and Ishikawa-Harima Heavy Industries Co. are making efforts to increase production capacity to meet the growing demand of the Chinese market and other markets.
Semiconductor components
The technical revolution in the field of semiconductor components in the 1980s led to a rapid improvement in the quality and functionality of Japanese electronics products. In the mid-1980s, Japanese companies became the world’s leading suppliers of semiconductor components.
Leading the industry are 3 telecom equipment manufacturers (Fujitsu, Nec, Oki Electric), 3 electronics manufacturers (Hitachi, Toshiba, Mitsubishi Electric), 4 manufacturers of consumer electronics (Matsushita Electric, Sanyo). Electric, Sony, Sharp). In particular, Fujitsu is the company that contributed to the miraculous growth period in Japan.
Steels and metals
Japan exported about 2.67 million tons of steel in 2018 down 14.7% from the same month last year. This volume decreased by 12.8% compared to August 2018.
This is also the first time since April 2018, the country’s steel export volume monthly fell below 3 million tons. In terms of exports, in September 2018, Japan earned 265.5 billion JPY from steel exports, up 0.6% compared to the same month last year.
5.What does Japan import?
This Chapter is for the ones, who are looking to start importing products into Japan or for those overseas, who are looking to find the right product to export to Japan. We will give a list of the main product categories here.
Japan develops diversified industries and with a high standard of living, so the demand for imported products is also diversified with various types of goods.

Main import products of Japan
- Pharmaceuticals: all kinds of medicines and solutions for curing and preventing diseases
- Telephones and parts, phone components, machines, and devices
- Portable data processing machine
- Vehicles of all kinds
- Cereals
- Seafood
- Wood and wood products
- Plastics and products
- Minerals and mineral fuels
In addition to mineral fuels, machinery, food, chemicals, and raw materials, etc., are the main imported products of Japan.
The main import markets of Japan are: China, the USA, Korea, Australia, Saudi Arabia, Malaysia, Germany, Taiwan, Indonesia, etc.
The situation in the main import industries in Japan
Seafood
Japan is the second-largest seafood importer in the world after the United States, the leading importer in Asia, and also the country with the highest consumption per capita in the world (67 kg/person/year). The Japanese attach great importance to the protein supply from fish and shrimp, especially during the year, the Japanese have hundreds of festivals and each festival has almost one or a few dishes made from seafood.
The Japanese market is very important to manufacturers of value-added shrimp products in Southeast Asia. In 2018, Japan imported 139,000 tons of shrimp from ASEAN countries worth 1.46 billion USD, equivalent to 67% of the volume and value of total shrimp imports of this country.
Exporting seafood to Japan needs to follow the technical barriers set by the Government of Japan to control the goods imported into this country. Compared to other countries, the technical barriers that Japan imposes are much stricter due to the consumption characteristics of the Japanese market.
Rice
Domestic rice prices are rising in Japan, prompting consumers to move towards the cheaper imported rice segment. Rice imports in Japan are strictly controlled. But as more supermarkets and restaurants offer low-cost imported rice, foreign rice producers expect to be able to call on Japan to expand its rice market.
Plastics
The annual import demand for plastic products in Japan is about $8 billion, so Japan is a potential market for plastic exporters.
In the near future, products that have traditionally used materials from glass, wood, paper, such as bottles, jars, cabinets, etc. will be replaced with products made from plastic. Therefore, in order to develop the plastics industry and export business sustainably, businesses need to have a strategy of investing in modern technology, product research, and prospecting of potential markets.
Tea
In 2010-2014, Japan spends about $ 100-200 million to import tea. In 2014, Japan ranked ninth in the world in terms of tea import, accounting for 2.93% of the world’s tea import turnover, with 189.62 million USD, down 2.85% compared to the same period in 2013. China, Sri Lanka, and India are the three main export markets for tea to Japan, accounting for 85.5% of the country’s total tea import turnover.
Ceramics

Japan is particularly fond of glazes, 3-color ceramics, table flower pots, ceramics, and tea (tea drinks).
Japanese market prefers thin, light ceramic, compact size. Thin ceramic is always the first choice of importers.
According to the Japanese Industrial Standards Act (JIS), “Products with Ceramic Ware Safety Mark” when exported to Japan will be tested for lead in their products.
Woods
The demand for wood pellets comes in Japan is mainly due to reducing the dependence on traditional fossil fuels as an energy source.
Japan is expected to build 43 highly efficient power plants in the next 10 to 12 years.
The strong expansion of power capacity is a boom for biomass wood pellet producers, as the strict emission targets for these new thermal power plants will almost certainly create the demand for wood pellets.
Japan requires all imported wood pellets to be certified Forest Management (FM).
6. High potential, small scale export-import business ideas

You may be thinking…with small and medium capital, are there any small-scale export-import business ideas regarding highly populous Japan, to execute and still achieve huge profits? Of course, there are and in the following list, we will give you many ideas to consider for your future business.
Japanese Cosmetics Business
Along with Korea, Japan is also a producer of cosmetics that are trusted by all Asian countries. Excellent products imported from Japan such as lotions, essential oils are very popular in China, Vietnam, Thailand, Laos, etc.
When importing Japanese cosmetics, you do not need to prepare a large amount of capital if you do business online or offline with high-quality cosmetic lines, from high-end brands to affordable brands from Japan. With great appeal to Asian customers and a good marketing strategy, you can achieve a profit that is many times bigger than the amount you spent.
Japanese Clothing Business
If you understand the fashion trends of the target customers that the brand wants to reach, and the know-how to reconcile the flow of domestic Japanese goods, the profits can be greatly increased. Japanese fashion is famous for its elegance and high quality.
E-commerce
Starting an e-commerce business is considered a safe option because if it fails, it will not cause a big loss of investment and E-commerce works like other traditional business forms.
There are many ways to start an online retail business. Starting with products that serve essential needs, innovative products. With current consumer habits, consumers will look at online products before deciding to visit and purchase.

Import/export agent or agency in Japan
You are living in Japan or you are very familiar with this county? If so, then you have a great opportunity to start a solo business as an export-import agent. You can help foreigners find the local customers and make nice commission incomes from this. Or you can help Japanese exporters to find customers overseas and make a commission from this. All is possible as an export-import agent.
7. Start exporting business to Japan
If you have been chosen and validated the product to export to Japan, then the following step-by-step action plan gives you a framework for actually starting exporting to Japan.
Goods exported to Japan are controlled by a strict legal system for reasons of protecting national security interests, economic interests, or ensuring food safety and hygiene. When entering the Japanese market, you need to thoroughly understand and strictly comply with the import laws and regulations of Japan. Before starting exporting to Japan, always ensure your product complies with the Japanese rules and requirements.
You can follow these steps below to start exporting to Japan:
Step 1: Create the export business plan
Developing an export plan is a prerequisite for a good export strategy and is very necessary. It helps you seize opportunities and minimize risks. It will also help you organize and set up a logical action plan. The content of the plan can vary, but it should include only the relevant and important subjects of your business. Read also how to prepare an export business plan.
The business plans should include
- Assessing the Japanese market situation, outlining the overall picture of export activities, advantages, and disadvantages, capital requirements, human resources requirements.
- Choosing export methods. This choice must be convincing on the basis of analyzing the relevant situation.
- Setting specific targets and goals like how many products to export, how much to sell, how much to profit.
- Setting out measures and implementation strategies to achieve goals
- Managing the risks and impacts coming from foreign exchange rate
- The target of the export turnover ratio.
- The target of return on capital for export.
- Break-even point analysis for goods export.
Step 2: Select the goods for export to Japan
In order to know whether an item can be exported into Japan, you have to learn the needs of Japanese for the products and consumption, understand the specifications of the type, size, price, season and taste, the consumption habits of each region.
In general, most Japanese consumers like high-quality and affordable goods with attractive design. English is not common in Japan, so if possible, translate the item’s name into Japanese
Goods that require an import license must comply with customs procedures, regulations, and laws. For some export items with quotas, you must apply for quotas at the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry – METI).
The procedure for exporting raw materials, raw or semi-finished products is usually easier.
Step 3: Search for the traders/importers/clients and partners
In order to be able to export goods, in the process of researching the Japanese market, you have to find a partner. There are two kinds of partners you may need: Traders (wholesale buyers) or Customers/Clients (retail buyers).
The selection of traders should be based on the following characteristics: the reputation in the market, time of business, financial capacity, technical facilities, the distribution networks.
Besides, if you only want to sell to retail clients, you need to understand who your customers are. What value does your product or service bring to its customers? Read also how to get orders abroad and fulfill them
Step 4: Sign the contracts

In order to enter into a sales contract, the exporters and traders should have to go through a process of negotiation and signing the contracts.
However, many exporting businesses have reported a situation where their buying partners have not strictly implemented the signed contracts on payment. Many businesses are confused in resolving trade disputes in import-export activities as above.
In fact, there are many causes of contract disputes, including subjective and objective reasons. Many terms in the contract are not clearly specified, not carefully studied by businesses before signing. Besides, the factor of awareness of contract law is also limited.
Therefore, to avoid risks, you should find ways to check and find out if your business partner is trustworthy or not. Sometimes, do not be fooled by their flashy profile. One way to search for a business partner is by using the help of the Japanese chamber of commerce.
Step 5: Apply for a license to export goods.
Some countries will strictly enforce export licenses, so you need to know your country’s regulations to see if you need an export license or not, also determine whether your item meets the criteria and conditions for export. Without an export license, you would not be able to ship your goods.
Step 6: Prepare the goods for export
After receiving the customer’s (foreign)advance payment, you should start to prepare the goods which meet the quantity and requirements set in the contract. After having the container booking, you start to take the packing containers and check the goods twice before sealing. Please pay attention to this step to carefully check whether the container is cracked or damaged because it affects cargo safety.
Step 7: Pack the export goods and carefully mark the good’s codes.
You can cooperate with the technical team, factory workers to close the goods at the warehouse. Pay special attention to pallets and choose the right type, the right size, number carton layers to pack according to the regulations of the importer, mark symbols, and print on each package, etc. Most LCL goods must write shipping marks. Packing at the port is much more complicated with the paperwork and you must have the inspection staff examine it.
Step 8: Check the quality of the cargo
Before delivery, you are obliged to check the goods for quality, weight, packaging, etc. This is an important task as customer benefits will be guaranteed, preventing untimely negative consequences, defining the responsibilities of production stages as well as creating sources of goods to ensure prestige for exporters and manufacturers in trading relations.
The inspection of export goods shall be conducted immediately after the goods are ready for export packing at the inspection establishment. At the border checkpoint, the goods will be directly inspected by the customer or by a competent agency subject to the agreement of the two sides.
Step 9: Buy cargo insurance.
Transporting export goods often present risks and losses, so buying insurance for exported goods is the best way to ensure safety for export goods during transportation.
You can contact some insurance companies to buy insurance for your shipment. Usually, the insurance price will depend on the value of your goods.
Step 10: Customs procedures and documentation (this is applicable for Japanese importer)
To export goods to Japan, you must declare information to the General Department of Customs and apply for an import permit after conducting goods inspection procedures, costing about 5,000 JPY for inspection. After the inspection, the importer will be granted an import permit, the cost for each copy is about 400 JPY (if online declaration the cost will be 300 JPY, currently 90% of the import procedures of Japan made by computer)
Export documentation for Japanese custom
You must declare and submit to the customs or your Japanese partner the following documents according to form C5020 of Customs:
- Commercial invoice;
- Bill of lading;
- Certificate of origin – CO
- Packing certificates, freight receipts, insurance certificates and other necessary relevant documents depending on the specific item.
- Permits, certificates, etc. required by other laws and regulations (applicable to relevant laws and regulations);
- A written request for exemption or reduction of fees and taxes, which describes in detail the necessary information, relevant regulations, and laws;
- Customs tax receipts (if the goods are taxable).
Requirements for a commercial invoice when exporting goods to Japan
There must be a minimum of 3 copies of the commercial invoice. The invoice needs to be signed by the supplier and should include the following details:
- The ordinal number and label number of the package
- Descriptive information about the goods
- Insurance fee and shipping fee
- Place and time of invoice
- Place of destination and recipient
- Vehicle, vessel, container number
- Import license number
- The terms of the contract relating to the valuation of goods
Requirements regarding Bill of lading
For goods sent by sea, it is required to have at least 3 original signed bill of lading and 2 copies.
For goods sent by air, it is required to have 1 original bill of lading and 9 copies but no strict rules apply. If the actual shipping quantity exceeds the quantity stated in the order, the name and address of the notified person must be clearly stated. Information in the importer’s trust letter is usually only nominal but must include the name of the vehicle, intermediate and final recipient, the label and the serial number of the box, description of the goods, chemical composition, and including the entire mass and dimensions in metric.
Step 11: Delivery on board.
After finishing the clearance for the shipment (the goods have been liquidated), your next job is to provide bill details for shipping lines to the bill of lading. Transporting containers on board is the job of the shipping company (because they charge you fees). This step ends with you having to receive a bill of lading which may be the original bill (3 copies).
Step 12: Payment procedures
Payment is an important and final result of all export business transactions. The choice of international payment methods will directly affect the interests of exporters and importers. When preparing import and export goods lots, both buyers and sellers must agree and select an appropriate international payment method. Therefore, when doing import and export, you need to understand the international payment methods to apply appropriately to the working process.
Step 13: Resolve the complaints (if any)
If after the delivery, the customer has a grounded complaint, you can resolve it by one of the following methods:
- Make up for missing goods in the following batch.
- Money, exchange when the goods are broken, or repair the goods at your expense or insurance.
- Reduce the price for which the discounted amount is covered by the goods delivered at a later time.
For additional reading, we are suggesting to read export import business guide.
8.Start importing from Japan
Steps and instructions mentioned in this chapter will help you start importing business and especially importing goods from Japan. We assume you have already clarified the product you want to import from Japan.

Japanese goods have long been known for their good reputation, quality, and impressive design. Currently, consumers in the world are increasingly interested in the quality of goods, so Japanese goods are always preferred.
Ways for importing from Japan
Currently, there are many ways to get Japanese goods into your hands. These ways have their own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the needs and practical capabilities which you should consider, to choose the appropriate importing method.
Directly import goods from Japan
If you are in Japan, you can arrange to directly take goods from Japan for your business. In this way, you can go to find goods from the factory directly or from the distributors in Japan and then order and hire a shipping company to transport goods by sea or air to your country.
Direct importing can help control the quality of goods, its original source, and get goods at a cheaper price than importing goods from intermediaries.
Order from e-commerce websites in Japan
In addition to picking up goods directly in Japan, you can purchase goods on Japanese websites to facilitate pickup.
Japan has many popular websites that you can search for goods such as Kanebo, Nissen, Rakuten, Amazon Japan, or electronic goods in the websites Kakaku, Yamada Denki, Noppin, Yodobashi, …
Get goods from the Japanese agents
You can choose agents that provide hand-carried or bulk deliveries by sea, or by air and redistribute to small shops. However, the import of goods through shops and intermediaries costs more. Besides, you can also use the import service company to help you import goods from Japan. But this way will cost you much more than doing by yourself.
Steps to import goods from Japan
If you import goods yourself, you need to find the source of the goods in Japan and then sign a foreign trade (sales-purchase) contract with the supplier. The contract will specify the method of international payment, requirements, and terms for the products as well as the required documents provided together with the goods. The following steps will show, how to import goods from Japan
Step 1: Apply the import license
To import goods yourself, or even just a shipment from abroad, you must first have a business license to import the item. If you do not have a license, you can go through goods import service companies, customs services, and Customs Agents in your country to sign a contract to import the goods from abroad.
Step 2: Find reputable businesses to order goods
To ensure safety and small risk, you can cooperate with bigger, reputable, long-term enterprises, you will have less risk and other issues during the importing process. To select and validate possible suppliers, use our free supplier validation checklist.
Choosing and picking the right product for importing is not less important than picking the right supplier. You can create a list of products that has demand In your country and start researching online, comparing prices and content of each product.
Step 3: Register for specialized testing (if any)
Depending on the country, the import may require specialized inspection of imported products. Most focus on industries such as culture, health, animal and plant quarantine, food safety inspection, motor vehicle-motor vehicle registration, etc.
Therefore, to avoid the effort of importing goods that are not allowed to circulate in your country, before determining to sign a purchase contract, please ask the partner to send the product samples and register for inspection at the authorization place.
If the goods are not on the list of specialized inspection requirements, skip this step and proceed to the next step.
Step 4: Sign import order
After identifying the goods to import and picking the right supplier, the next step is to send a purchase order (PO), usually by email or other online forms. In the PO, you need to specify the following, but pay special attention to payment conditions:
- Full details about the seller (Company name, address, phone number, email, representative)
- Full details of the enterprise or the buyer (Company name, address, phone number, email, representative)
- Details of goods (Name of goods, quantity, delivery conditions, total amount, quality, design …)
- Price and delivery terms
- Terms and method of payment
When ordering, you should always ask the seller to send Proforma Invoice because Proforma Invoice will be the basis to transfer money from your bank (Depending on the payment conditions). Proforma you will also need later on for your custom.
Step 5: Sign a contract, plan the time to transport imported goods to your country
When the seller confirms the orders, both sides can sign the contract.
To ensure the safety of imported goods and to prevent any arising problems that may cause difficulties in the future, you should pay special attention to the following details in the contract:
- Name of goods, quantity – weight, specifications, prices, packaging, etc.
- What are the terms of delivery? For example, CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) is delivered at the port of discharge. FOB terms are (Free on board) – Delivery on board, etc.
- When is the delivery time?
- Term and mode of payment. For example, TT method – wire transfer, T / C method – letter of credit), etc.
- Types of necessary documents the seller must prepare to give to the buyer
- Other agreements and terms
Step 6 – Packing goods, delivery at seaport or airport
You need to track the process of packing and deliver goods at the port, such as the time of packing, how much it costs, how long it takes to transport from the factory to the port. This tracking can be done through websites or direct contact by phone, email, and other forms. Definitely ask the supplier to provide the photos and videos of the packing process.
Basic import documents include
- Bill of lading
- Commercial invoice
- Packing list
- Foreign trade contract
- Certificate of origin
- Other documents
Step 7: International cargo transportation by sea or air
Whether your shipment is shipped by sea or by air, you should pay attention to the following:
- Name of the carrier, contact number, web page to track the route of cargo schedule
- Schedule how many trips/week
- How long does shipping take?
- When is the latest delivery time?
- Departure / arrival date
- Go directly or transfer (direct / tranship)
- Departure port / destination port
- In the case of damaged goods, what to do if it is not compensated?
Step 8: Pay for the imported goods
The time for payment is based on the signed sales-purchase contract between the two parties.
In the international payment, you need to prepare the payment in accordance with what is stated in the contract and invoice. In addition, the information about the beneficiary, beneficiary bank name, and address must also match in the contract, invoice.
Step 9: Customs procedures for imported goods
When doing customs clearance, you first proceed to the Customs declaration after the shipping company sends a notice of arrival.
On the declaration, there will be a lot of information you need to fill out. All kinds of codes such as port codes, type codes, customs codes, etc., and many other details. You need to prepare carefully and complete the information. If you have just done the customs declaration for the first time, it is best to consult the guidance of experienced people to avoid making incorrect, missing entries, as well as time-consuming and unwanted system errors.
Step 10: Receive the delivery orders
After opening the Customs Declaration, the Customs will check your goods to see if it is in the Contract, Invoice, Packing List as well as C / O. If true, customs release the goods and you can transport them to your warehouse. Depending on the item, prepare to pay import duties, VAT, and other taxes after a certain time.
In some cases, there will be additional environmental taxes and excise taxes depend on each country’s law.
So the import procedure has been completed, then you can proceed to distribute those goods and earn a profit.
Conclusion
The procedure for importing goods from Japan for newbies seems to be quite complicated. So do not hesitate to learn from experienced people. Gradually you will become a master of imports.
If you want to learn how to start your own export-import business online or offline, then we have online courses and programs which will give you the best guide to start an international business from scratch. We have also tools and resources which help you to grow and expand your business and get more customers and raise profitability.
You are advised to take courses and use the resources ad tools listed below:
- Export-import business courses and programs
- Most popular online exim course: “Zero to first deal“
- Resources and action plan for exporters/importers, online sellers.

